Project in a nutshell
Increasing cooperation between the blue (maritime-led) and green (ecological, environmentally-friendly technologies-led) sector for development and launch of new innovative products, processes and services in our region.
Project partners will work on this idea during the project life from the following regions across the Baltic Sea:
- in Germany – districts (Landkreise) of Mecklen- burg-Vorpommern: Nordwestmecklenburg, Rostock, Vorpommern-Rügen, Vorpommern-Greifswald and district-free city (kreisfreie Stadt): Rostock;
- in Denmark – Regional Municipality of Bornholm and Region Zealand (subregions: Østsjælland, Vest- og Sydsjælland);
- in Sweden – counties of: Kalmar, Blekinge, Skåne and Kronoberg;
- in Lithuania – counties of Klaipėda, Tauragė and Telšiai;
- in Poland – subregions of: Miasto Szczecin, Szczeciński, Stargardzki, Koszaliński, Słupski, Starogardzki, Gdański, Trójmiejski and Elbląski.
Creative Traditional Companies Cooperation project is part-financed by the European Regional Development Fund(ERDF) within the South Baltic Programme 2007-2013.
Source: Laima Gerlitz
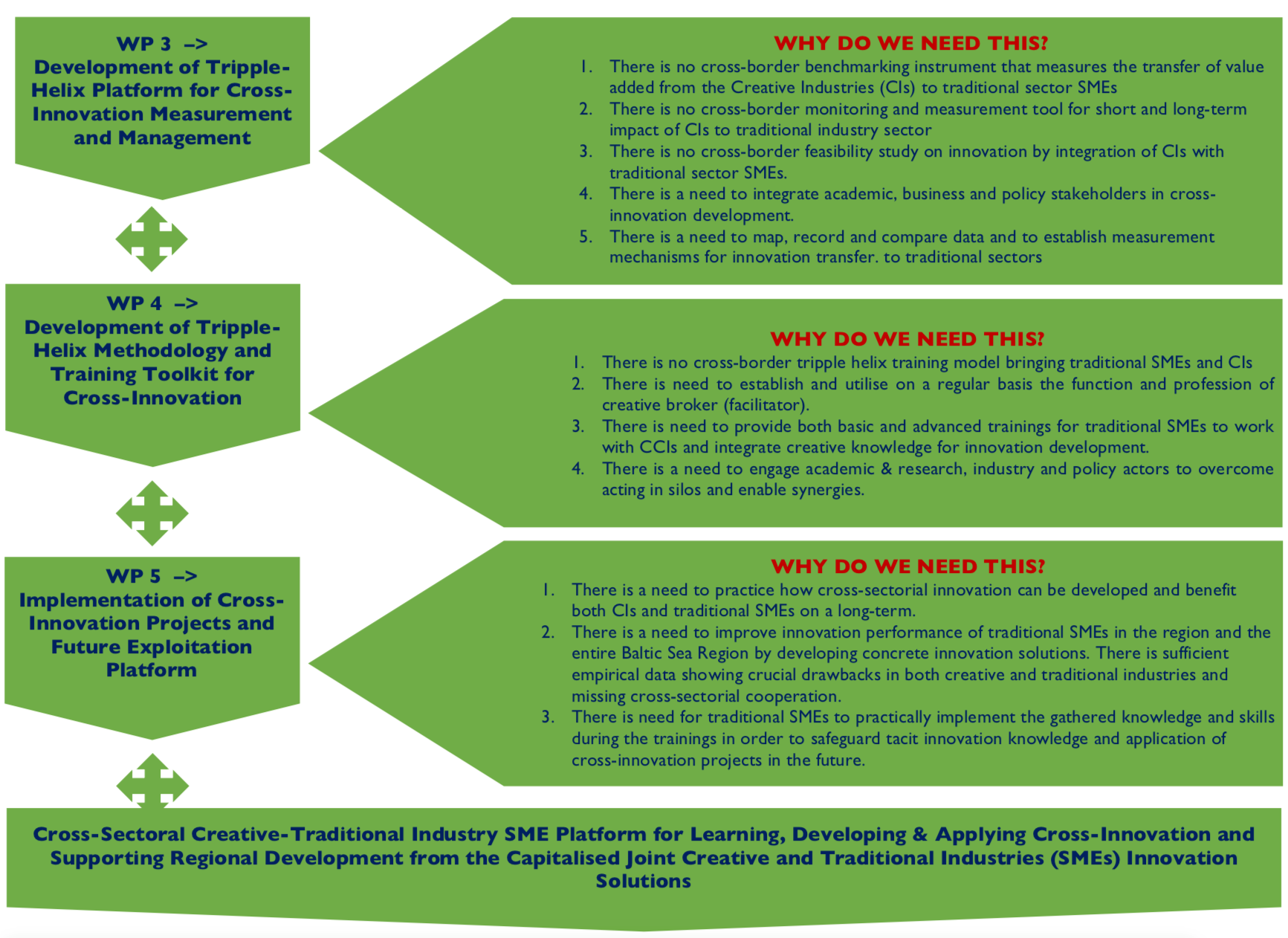
CTCC will improve innovation performance of minimum 200 Danish (DK), German (DE), Polish (PL), Lithuanian (LT) and Swedish (SE) small and medium- sized enterprises (SMEs) from the South Baltic Sea Region (SBSR) until 30th June 2020 from the three targeted traditional manufacturing sectors that contribute to blue and green growth – a) maritime transport & shipbuilding; b) green (renewable) energy production (offshore wind energy; biofuels, biogas) and c) maritime tourism (yachting, marinas and cruising infrastructure). The improved innovation of traditional SMEs is achieved by engaging in the cross-sectorial collaboration with 100 freelances, start-ups and SMEs from the three Creative Industries (CI) sectors d) design (industrial, graphic, interior and interaction), e) architecture (e.g. naval architects) and f) advertising and software & games. Cross-sectoral creative-business partnership (cross-collaboration) will deliver 30 specific demand-driven innovation solutions for the traditional SMEs and regions within product, service, organisational or positioning (marketing & sales) field . We will work with the 3 selected sub-sectors from the overall 11 Creative and Cultural Industries (CCIs) sectors, because the project aims at delivering industrial innovative solutions for manufacturing SMEs, and usually needs industrial or product designers, (naval) architects and engineering designers.
The solutions concern industrial side of products, organisational or marketing (sales) process, e.g. using materials advantage, reducing materials usage, switch to environmental and recoverable or renewable materials use for innovation development. The project targets from the 17 spill-over types (rf. https://ccspillovers.wikispaces.com/file/view/Cultural+and+creative+spillovers+in+Europe+-+full+report.pdf) only industrial spill-overs – improving business culture and boosting entrepreneurship, stimulating investments, improving productivity, profitability and competitiveness, and boosting innovation and digital technology. Therefore, the innovation solutions will be clearly measured after the project life by the number of minimum 30 developed innovations – developed prototypes of innovative products, services, organisation improvement or positioning (marketing) innovation incl. business models. Indeed, speak about the prototypes, since the place of innovation developed on the market and exploited can be only called in the science and practice terms as innovation. Practically, development of tangible innovation solutions includes delivery of the following components (four key project pillars) that belong to the overall cross-innovation portfolio:
1) Developing of the reliable and comparable triple-helix creative-traditional partnership platform dedicated to management and measurement of crossovers and industrial spill-overs from the selected CI to the targeted traditional SME sectors. The platform will integrate all region-wide knowledge, data, analysis and impact on crossovers among the selected traditional and creative sectors. It will showcase potential how to better use creative tools, methods, innovation development approaches and their contribution to capture innovation in the traditional manufacturing sectors that are lagging-behind in innovation performance or are slowly developing in terms of the need to contribute to the blue and green growth.
2) Transfer of the innovation development skills and knowledge from cross-sectorial interactions to min. 200 traditional SMEs and 100 CI representatives in the frame of joint trainings. This will include cross-innovation basic and advanced training methodology, creative broker network, creative auditing methodology and its feasibility study. Both traditional SMEs and CI representatives will benefit by getting knowledge, skills and tools from the sector, which is rather unfamiliar to them and where they miss the competences to successfully engage into innovation development and enter the markets.
3) Increasing tacit knowledge on cross-innovation opportunities in the SBSR by developing joint crossovers with 200 traditional SMEs and 100 CI representatives – 15 innovation solutions and 15 business models.
4) Developing future platform for regular crossovers exploitation – a) running yearly Innovative Entrepreneurship Contest – cross-innovation competitions between traditional and creative sectors; b) developing University-Business Partnership – integrating CTCC Platform and creative audit tool in academic curricula and activities by means of e.g. academic graduation thesis proposals by traditional SMEs to be developed in cooperation with university students, or publication of projects on university and professors websites, incl. CTCC platform placement on all project academic partners’ websites; c) developing triple helix training and retraining programmes for traditional or creative professionals involving academia & research, business, intermediaries and authorities; d) developing cross-border competence mobility centres for crossovers and cross-innovation located at intermediaries (e.g. chambers of commerce, incubators) and e) providing policy-makers with the future guidelines on exploitation of the cross-innovation potential to boost regional economy in the SBSR and outside.
